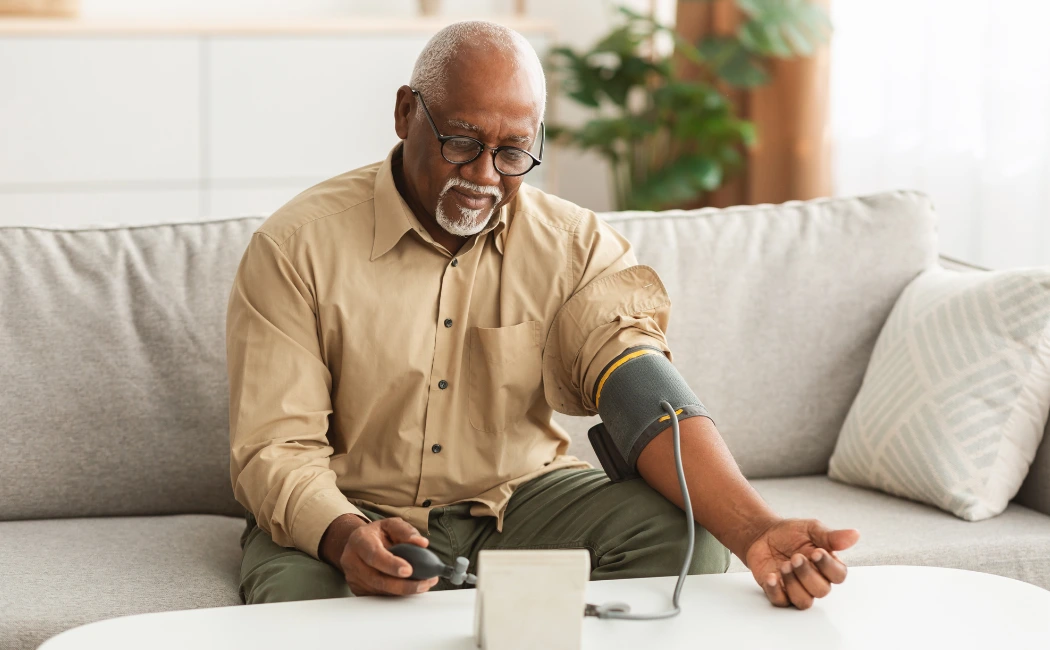
High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, affects millions of people worldwide.
Managing this condition requires a combination of lifestyle changes, medication, and dietary modifications.
Certain foods can exacerbate high blood pressure, increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease, stroke, and kidney damage.
In this article, we’ll explore the foods to avoid when living with high blood pressure.
You May Also Like: Breaking Free from Digital Overload: The Digital Detox Movement
Understanding High Blood Pressure
Before diving into the foods to avoid, it’s essential to understand high blood pressure:
- High blood pressure: 140/90 mmHg or higher
- Normal blood pressure: Less than 120/80 mmHg
- Prehypertension: 120-139/80-89 mmHg
Foods to Limit or Avoid
- Sodium-Rich Foods
- Processed meats (bacon, sausages)
- Canned goods (soups, vegetables)
- Pickled foods
- Soy sauce
- Teriyaki sauce
Recommended sodium intake: Less than 2,300 mg/day
- Saturated and Trans Fats
- Red meat (beef, pork)
- Full-fat dairy products
- Processed snacks (chips, crackers)
- Fried foods
- Baked goods
- Cholesterol-Rich Foods
- Egg yolks
- Organ meats (liver, kidney)
- High-fat dairy products
- Shellfish (shrimp, lobster)
- Refined Carbohydrates
- White bread
- Sugary drinks
- Refined grains (pasta, rice)
- Processed snacks
- Caffeine and Alcohol
- Excessive caffeine consumption (more than 2 cups/day)
- Alcohol (more than 1 drink/day for women, 2 drinks/day for men)
Why These Foods Are Harmful
- Sodium increases blood pressure
- Saturated and trans fats raise cholesterol levels
- Cholesterol-rich foods increase cardiovascular risk
- Refined carbohydrates cause inflammation
- Caffeine and alcohol can raise blood pressure
Healthy Alternatives
- Fresh fruits and vegetables
- Whole grains (brown rice, quinoa)
- Lean proteins (poultry, fish)
- Low-fat dairy products
- Healthy fats (avocado, olive oil)
Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH)
The DASH diet is specifically designed to help manage high blood pressure:
- Emphasizes whole grains, fruits, vegetables, lean proteins
- Limits sodium, saturated fats, cholesterol
- Encourages moderate caffeine and alcohol consumption
Conclusion
Managing high blood pressure requires a comprehensive approach, including dietary changes.
By avoiding or limiting harmful foods and incorporating healthy alternatives, individuals can reduce their risk of cardiovascular complications.
References:
- American Heart Association. (2020). High Blood Pressure.
- National Institutes of Health. (2020). High Blood Pressure.
- Mayo Clinic. (2020). High Blood Pressure.
- Harvard Health Publishing. (2020). Foods to Avoid with High Blood Pressure.
- Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics. (2020). High Blood Pressure.
Additional Resources:
- American Heart Association: High Blood Pressure
- National Institutes of Health: High Blood Pressure
- Mayo Clinic: High Blood Pressure
- Harvard Health Publishing: Foods to Avoid with High Blood Pressure
- Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics: High Blood Pressure